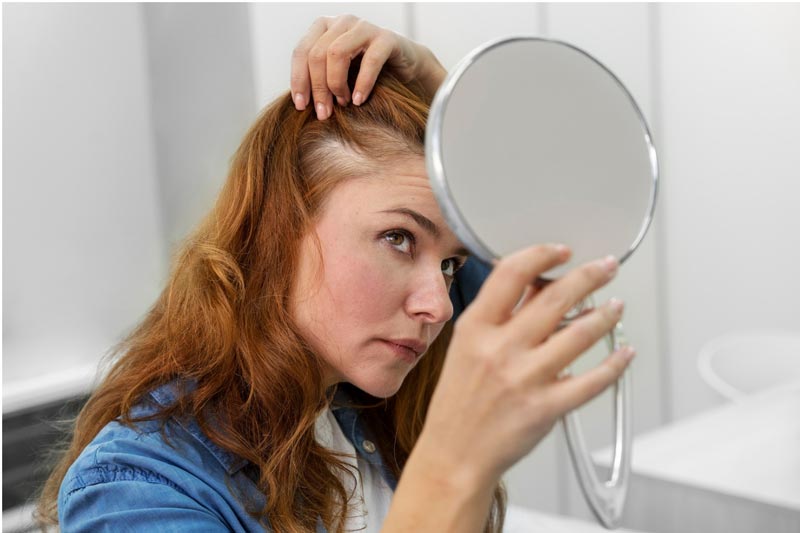
It is very common for many women to experience hair loss after giving birth. In fact, this phenomenon, known as postpartum alopecia, is a disorder that has been studied for a long time to understand its causes and find possible solutions.
Since the 1960s, it has been considered that, in contrast to other types of alopecia, postpartum hair loss is not a hereditary problem. Some studies have observed that it begins between 8 and 16 weeks after giving birth and that, in most cases, it takes 4 to 6 months to return to normal. However, it should be noted that almost all women recover normal hair growth over time (Arch Dermatol. 1963;87(5):609-611).
Postpartum hair loss is included in what is known as telogen effluvium, consisting of an alteration that leads to a sudden loss of hairs that were in the growth phase, called the anagen phase, and that pass to a shedding phase, telogen phase. While the loss of about 100 hairs a day is considered normal, in cases of telogen effluvium the number triples.
During gestation, estrogen levels are elevated, but decrease significantly after delivery to return to normal values. Specialists explain that this reduction in female hormones is one of the main causes of hair loss after giving birth. But it is not the only one, since emotional states, such as stress or certain traumatic events, also influence it, constituting one of the most important causes of the aforementioned telogen effluvium in general, especially in women.
What can we do about hair loss?
Hair care is essential to alleviate hair loss. In addition, there are some habits that can help improve hair health. It is advisable to avoid exposure to high temperatures (such as hair dryers or hair straighteners), and it is preferable to dry naturally in the air after washing, and brushing should not be overdone. It should also be taken into account that some types of hairstyles favor breakage or hair loss, so it is preferable to wear your hair loose and avoid braids, buns or very tight ponytails.
Among the recommendations highlighted by experts in this situation, diet plays a fundamental role. The diet must provide the nutrients that the woman’s body needs after becoming a mother, so fruits and vegetables – always advisable in any type of diet – become especially important along with healthy proteins. In this context, some foods such as carrots (which contain beta-carotene), green leafy vegetables (rich in vitamin C and iron), eggs (for vitamin D) or fish (rich in omega-3 fatty acids and magnesium) will help make hair healthier.
Pilopeptan® postpartum supplements
To reinforce the intake of fundamental nutrients, supplements may also be necessary, and there are products specifically formulated to prevent hair loss in women and recover their growth as soon as possible.
These include Pilopeptan® Intensive and Pilopeptan® Woman Tablets. The first, in the form of drinkable sachets, has a high content of hydrolyzed collagen, a substance that reinforces the anchoring of the hair in the hair follicle, thus stopping its fall. The second, in tablet form, contains hydrolyzed collagen, hyaluronic acid, B vitamins, sulfur amino acids such as L-cystine and L-methionine, as well as minerals such as zinc, iron and selenium.
In a clinical trial that evaluated the combination of these products in a group of 160 women with telogen effluvium, it was found that taking a sachet of Pilopeptan® Intensive daily for one month, as a shock treatment, and then continuing with Pilopeptan® Woman Tablets for three more months, as a maintenance treatment, reduces hair loss and promotes the recovery of the growth phase or anagen phase. The results showed statistically significant improvements from the first month.
In any case, as we have already mentioned, postpartum hair loss or postpartum alopecia is a process that resolves over time in most women. However, the recommended tips and products are an invaluable aid to make recovery faster and easier.
Bibliography
1. Study of postpartum alopecia.Schiff BL, Kern AB. Arch Dermatol. 1963;87(5):609-611.
2. Moreno, G et al. Effectiveness of a food supplement on hair and nail health in women with telogen effluvium. Combination of a shock treatment and a maintenance treatment: preliminary study. National Congress of Dermatology and Venereology. Palma de Mallorca, 2018.